What is a Data Core?
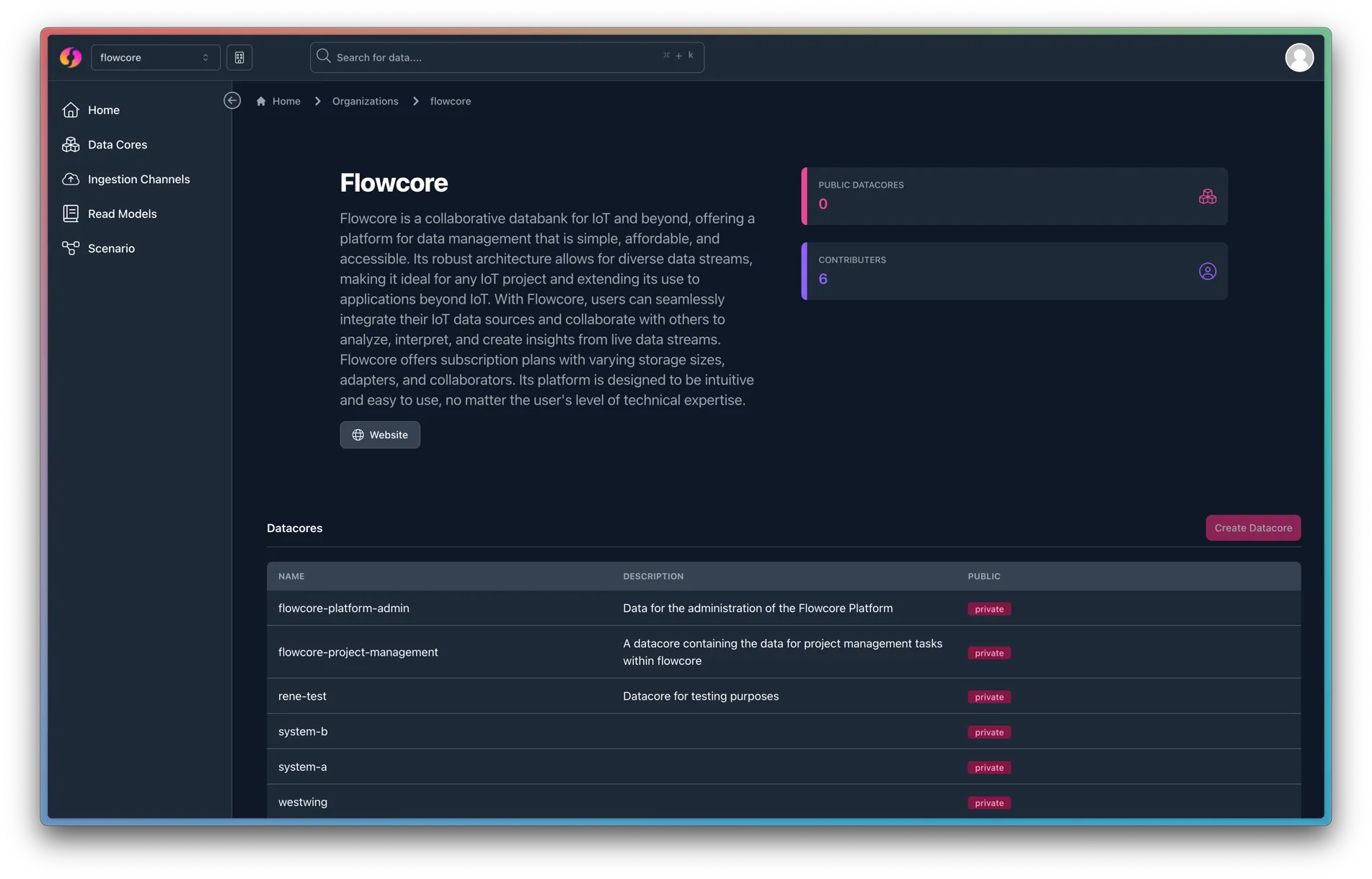
A Data Core is essentially a log book for unstructured data. Meaning that you can send data to a Data Core without having to decide the exact model for your data. Instead you send in any and all information that could be relevant, and the Data Core will store it for you. Notice the mention of a log book. This is because a Data Core is a chronological log of all the data that has been sent to it. This means that you can send in data at any time, and it will be stored in the Data Core in the order it was received.
With these two strengths, asyou are able to send in any data, and then decide at an unspecified time, what you wish to use the data for, and what specific data you need. This is done by pulling data from a Data Core into an Adapter.
Bear in mind that the data is never altered, meaning that you always have a full history of the data inserted into a Data Core. When you pull the data out using an Adapter, you are still not altering the data, but rather copying it.
To send data to a Data Core, you use an ingestion channel.
Within the Data Core, you can organize your data further by creating groups and subgroups. This is done by creating Flow Types from within the Data Core, and Event Types within the Flow Type.
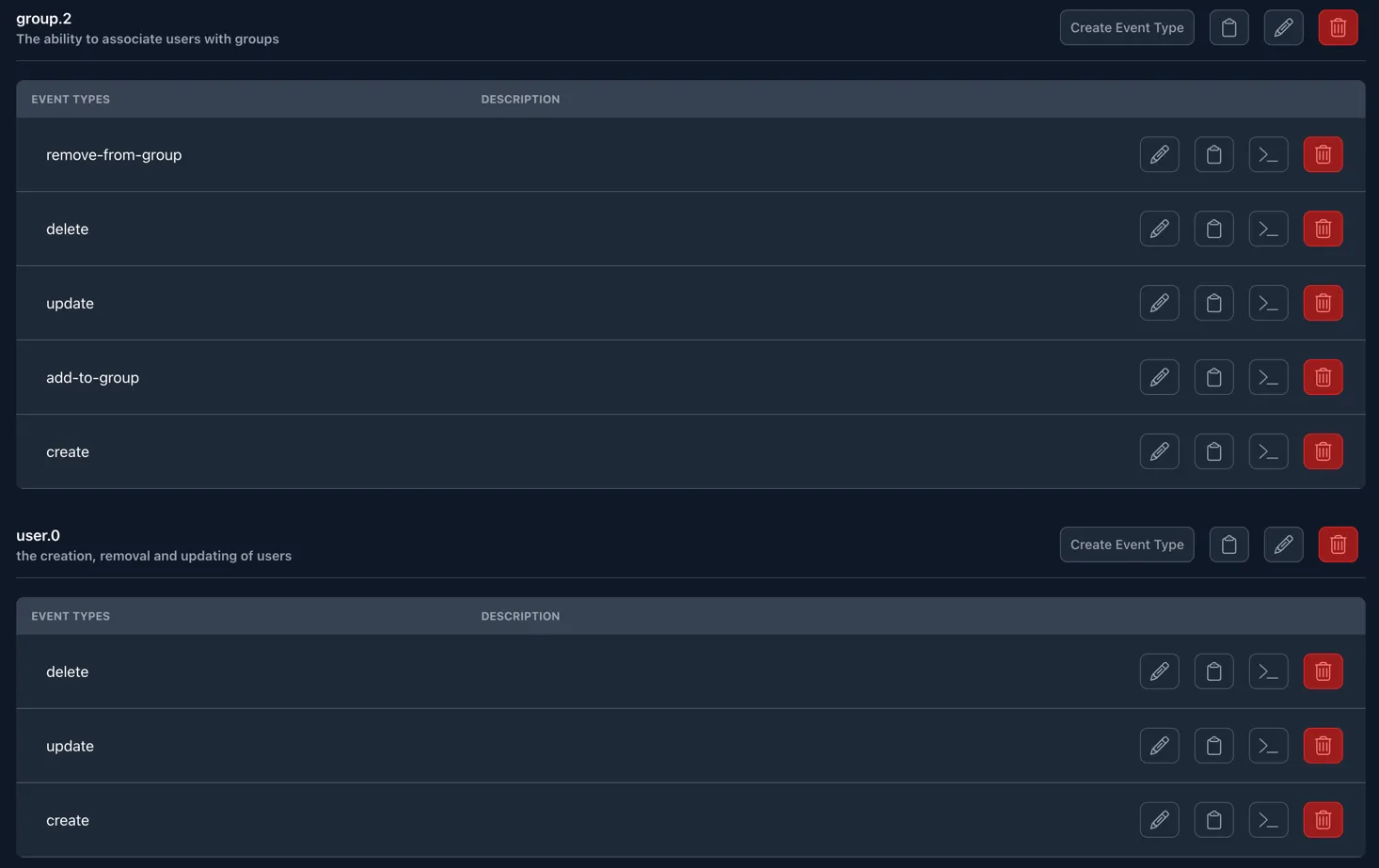
What are Flow Types & Event Types?
To simplify the concept of Flow Types, you can imagine that the aggregator is a drawer and the Event Types are little storage boxes within the drawer. This gives you the ability to roughly organize your data without having to be too thorough. Allowing you to group up multiple related data sets into one Data Core.
Access availability
There are two access availabilities for Data Cores:
Public- Anyone using flowcore can subscribe to your public Data Cores and access the data within it. They cannot send data to your Data Core without an API Key that you have granted them
Private- Any collaborators you invite to your organization can access your private Data Cores. They cannot send data to your Data Core without an API Key that you have granted them
There is no limit to how many public Data Cores you can create. However, you are required to buy private Data Cores.
Public Data Cores are ideal for:
- Data that you don’t mind being public, such as:
- some irrelevant test data
- Data that you would like to be accessible to the world to utilise, such as:
- Weather data
- Traffic data
- High-scores
- etc
Private Data Cores are ideal for:
- Internal Company data, such as
- user
- or financial information
- etc
- Personal data, such as
- financial data
- or my acne status
- etc